Tailwind Design Patterns
SVG Scaling
Intent
The goal is to scale an SVG element to fit its container while maintaining the aspect ratio.
Problem
The width and height attributes of an SVG element may not necessarily scale the element to fit its container. This can be seen in the following example:
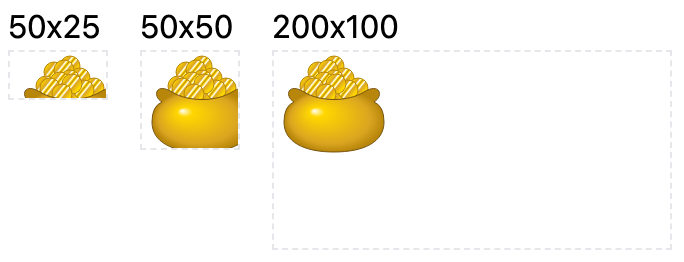 https://codepen.io/PengXiao/pen/xxJxagZ
https://codepen.io/PengXiao/pen/xxJxagZ
Example in ZenUML
ZenUML allows you to assign icons to participants. These icons are represented as SVG elements. In the following example, we use an EC2 icon for the OrderService participant and a Boundary icon for the MainFrame participant:
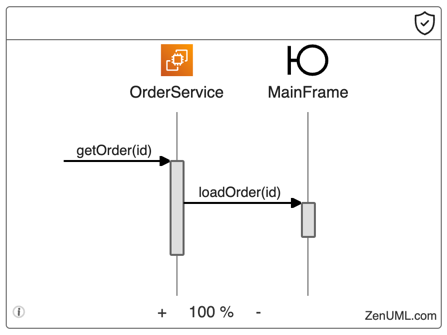
Solution
To properly scale the SVG, we can use the viewBox attribute. The viewBox attribute defines a coordinate system and a clipping region for the SVG. The element will be scaled to fit within the clipping region. Many editors (such as Figma or Sketch) will automatically add the viewBox attribute to an SVG, but if it is missing or incorrect, you can use the "resize to fit" feature in Figma to fix it.
We can then control the size of the SVG by setting the width and height attributes. However, it is a good practice to use width: 100% and height: 100% to allow the SVG to scale to fit the container.
<div class="icon w-8 h-8 [&>svg]:w-full [&>svg]:h-full">
<svg viewBox="x y w h">
<!-- svg content -->
</div>
https://codepen.io/PengXiao/pen/gOjOQzL
Let me explain the tailwind CSS classes one by one:
w-8andh-8: Set the width and height of the container.[&>svg]:w-fulland[&>svg]:h-full: Set the width and height of the SVG element to 100%.
Discussion
The key to successfully scaling an SVG is the use of the viewBox attribute. Without this attribute, the SVG will not scale to fit its container. By using viewBox, we can ensure that the scaling is natural and does not stretch or distort the element.